

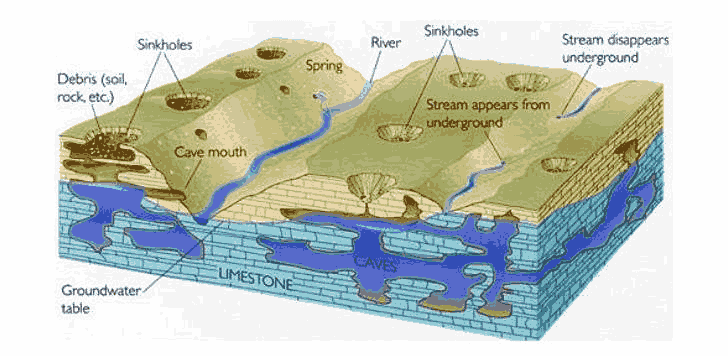
Karst topography is a fascinating geological phenomenon characterized by unique landforms.
Karst topography is a fascinating geological phenomenon characterized by unique landforms that arise primarily from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, gypsum, and salt. This article delves into the different formations associated with karst topography, specifically focusing on caves, kettles, meanders, and oxbow lakes. By exploring these features, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of their formation processes and significance within karst landscapes.
Caves are one of the most iconic features of karst topography, forming through the slow dissolution of soluble rocks. Limestone caves are particularly prevalent in karst regions due to the high solubility of limestone in acidic solutions. The process begins when rainwater, slightly acidic from dissolved carbon dioxide, seeps into the ground and comes into contact with limestone. Know the deepest cave in the world.
Caves not only contribute to the aesthetic and scientific value of karst landscapes but also serve as critical habitats for a variety of species. They provide unique ecosystems and have significant archaeological and paleontological importance, often preserving ancient artifacts and fossils.
Kettles are depressions or holes in the ground formed by the melting of glacial ice. Although they are not exclusive to karst landscapes, they can occur in karst regions where glacial activity has interacted with the underlying soluble rock formations.
Kettles contribute to the hydrological and ecological diversity of karst landscapes. They can create habitats for various species and influence local hydrology by altering drainage patterns.
Meanders are bends or curves in river channels that are shaped by the lateral erosion and deposition processes. While meanders are not exclusive to karst landscapes, they can significantly impact karst terrain by modifying drainage patterns and creating distinctive landforms.
Meanders play a crucial role in shaping the landscape and influencing sediment transport. They also create diverse habitats for aquatic and terrestrial species, contributing to the ecological richness of river systems.
Oxbow lakes are crescent-shaped lakes formed when a meander in a river is cut off from the main channel. They represent a dynamic stage in the evolution of river systems and can be found in both karst and non-karst landscapes.
Know the fact about: is water wet?
Karst topography is a dynamic and diverse landscape shaped by a variety of geological processes. Caves, kettles, meanders, and oxbow lakes each contribute uniquely to the formation and evolution of karst regions. Understanding these features provides insight into the complex interactions between geological processes and landscape formation.
