

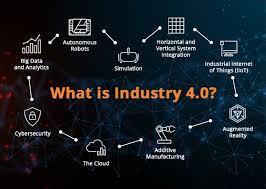
What is industry? Industry, in the broadest sense, refers to the production of goods and services within an economy.
What is industry? Industry, in the broadest sense, refers to the production of goods and services within an economy. Traditionally, it has encompassed various sectors including manufacturing, agriculture, construction, mining, and services. Industries lie at the core of societal development and significantly contribute to the advancement of technology, economic growth, and the quality of life. Over the years, industry has undergone tremendous transformations, evolving from simple manual production systems to technologically advanced, interconnected frameworks. Today, we are witnessing a new era in industrial evolution known as Industry 4.0. This article explores the meaning of industry, traces its historical evolution, and provides insight into Industry 4.0—an intelligent blend of cutting-edge technologies that are shaping the current industrial landscape.
What is Industry?, at its simplest, is an organized system of economic activity designed to produce goods or deliver services. The term “industry” was originally applied to manufacturing activities, but it has since broadened to encompass virtually every sector contributing economic value, including health services, education, financial services, and technology development. Fundamentally, an industry relies on human labor, capital investment, natural resources, and technological innovation for its operation and growth.
Historically, industries have been classified into the following types:
The history of industry as we know it today can be divided into key phases marked by transformative advancements. These phases are often referred to as industrial revolutions. Let’s explore the journey leading up to Industry 4.0.
The first industrial revolution began in the late 18th century with the advent of mechanization and the replacement of manual labor by machines. Central to this phase was the invention of the steam engine, which powered factories, production lines, and transportation systems. This revolution shifted the focus from agrarian economies to industrial manufacturing, leading to urbanization and significant economic growth.
Key inventions like the spinning jenny and steam-powered engines paved the way for increased productivity in the textile and iron industries. However, this phase also brought challenges such as poor working conditions, long hours, and environmental degradation.
Often referred to as the age of electricity, the second industrial revolution was driven by the widespread use of electric power and the innovation of assembly lines. These advancements further increased productivity and made mass production viable. During this period, industries such as steel, chemicals, and petroleum thrived, supported by advancements in transportation systems like railways and automobiles.
The increase in industrial output during this phase led to improved standards of living for many, but also introduced new challenges such as monopolies and inequalities in wealth distribution.
The third industrial revolution, often called the digital revolution, marked the transition from mechanical and analog systems to digital technologies. Computers, microprocessors, robotics, and the Internet began to play a central role in industrial operations. Automation became a cornerstone of manufacturing processes, optimizing productivity and reducing human intervention in repetitive tasks.
This era saw industries evolve toward globalization, as technological advancements allowed businesses to operate across borders and access new markets. However, the reliance on fossil fuels persisted, and environmental concerns began to emerge.
So, what is industry? It is an ever-evolving system that has fueled human progress for centuries. From the first industrial revolution driven by steam engines to the emergence of Industry 4.0 built on smart technologies and interconnectivity, the journey of industry is a testament to humanity’s ingenuity and drive toward innovation.
