

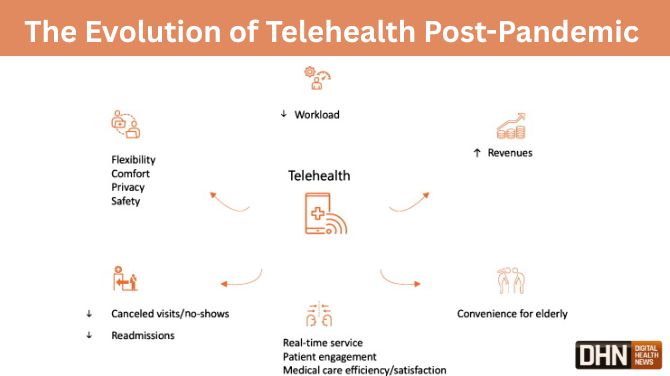
The evolution of telehealth post-pandemic reflects a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery.
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed a seismic shift in healthcare delivery, thrusting telehealth into the spotlight as a vital tool for patient care. As we navigate the post-pandemic landscape, telehealth continues to evolve, reshaping how healthcare services are accessed and delivered.
Prior to the pandemic, telehealth accounted for a minimal fraction of healthcare interactions. However, the onset of COVID-19 necessitated rapid adoption of remote care solutions. In the United States, telehealth visits among Medicare recipients skyrocketed from approximately 5 million to over 53 million in 2020 alone. This surge was mirrored globally, as healthcare systems sought to maintain continuity of care while minimizing infection risks.
While the initial spike in telehealth usage has stabilized, it remains significantly higher than pre-pandemic levels. Data indicates that telehealth utilization has settled at rates 38 times greater than before the pandemic, with approximately 13% to 17% of all patient visits conducted virtually. This sustained usage underscores telehealth’s integral role in modern healthcare delivery.
Advancements in technology have been pivotal in enhancing telehealth services. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and remote patient monitoring (RPM) has enabled more proactive and personalized care. AI-driven RPM systems facilitate continuous monitoring of patients’ health metrics, allowing for timely interventions and improved outcomes. Additionally, the proliferation of user-friendly telehealth platforms has improved accessibility and patient engagement.
Despite its benefits, telehealth faces challenges, particularly concerning equitable access. Rural communities and underserved populations often encounter barriers such as limited internet connectivity and digital literacy. Efforts to bridge the digital divide are essential to ensure that telehealth services are inclusive and accessible to all segments of the population.
The rapid expansion of telehealth prompted temporary regulatory flexibilities to accommodate remote care delivery. As the public health emergency subsides, policymakers face decisions regarding the permanence of these changes. Advocates argue for the continuation of supportive policies, including reimbursement parity and cross-state licensure, to sustain telehealth’s momentum and integration into standard care practices.
Looking ahead, telehealth is poised to further transform healthcare delivery. Emerging models, such as virtual hospitals, exemplify the potential for comprehensive remote care. For instance, Seha Virtual Hospital in Saudi Arabia has become the world’s largest virtual hospital, coordinating with 224 hospitals and offering 44 specialized services. Such innovations highlight telehealth’s capacity to enhance access, efficiency, and patient outcomes on a global scale.
The evolution of telehealth post-pandemic reflects a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery. By leveraging technological advancements and addressing challenges related to equity and regulation, telehealth can continue to expand its reach and efficacy. As we embrace this digital transformation, telehealth stands as a cornerstone of accessible, patient-centered care in the modern era.
