

Pneumatic Wafer Butterfly Valves: Structure, Features, Applications, and Maintenance
Pneumatic wafer butterfly valves have become essential components in many industries due to their efficient flow control, compact design, and ease of use. As one of the most widely used types of control valves, they are prized for their lightweight construction, rapid operation, and high reliability. Their structural versatility and straightforward installation make them ideal for a broad range of applications—from chemical processing plants to water treatment facilities.
This article explores the structure, key features, industry applications, installation procedures, maintenance tips, and operational guidance for pneumatic wafer butterfly valves. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of why these valves are an indispensable choice in modern fluid control systems.
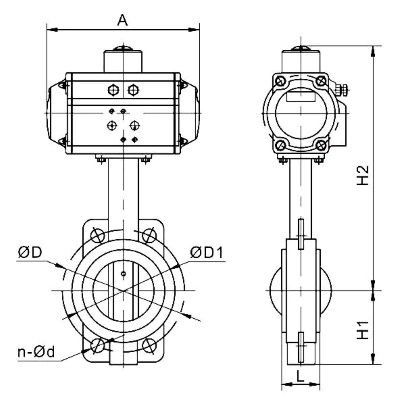
Pneumatic wafer butterfly valves consist of two main components:
A pneumatic actuator, powered by compressed air
A butterfly valve body, containing a rotating disc for flow control
The “wafer” designation refers to the installation method—sandwiched between two pipeline flanges, secured with bolts that pass through both flanges and the valve body.
When compressed air enters the actuator, it rotates the valve stem and disc. The disc’s angle determines whether fluid flow is allowed, throttled, or blocked. This mechanism enables fast response, precise control, and seamless integration into automated systems.
Compact & Lightweight
Easy to transport, install, and maintain
Reduces stress on pipelines and support structures
Easy Installation & Maintenance
Installed between flanges with fewer bolts than lug-type valves
Simplified disassembly and part replacement
Simple, Efficient Structure
Fewer components reduce failure risks and improve reliability
Low Operating Torque
Disc design reduces flow resistance and actuator size
Quick 90° Rotation
Fast opening and closing for high-cycle operations
Excellent Flow Characteristics
Minimal pressure drop and good throttling performance
Pinless Disc-to-Stem Connection
Prevents leakage and enhances structural durability
Spherical Disc Profile
Ensures uniform sealing and extends seat life
Replaceable Sealing Components
Allows for cost-effective maintenance and long service life
Disc Coating Options
PTFE, nylon, and other coatings for chemical resistance or food-grade applications
Flexible Connections & Actuation
Available in flange versions; supports manual, electric, or pneumatic operation
Chemical Processing
Handles corrosive and hazardous media reliably
HVAC Systems
Regulates airflow and chilled water efficiently
Water Treatment
Manages clean water distribution and wastewater systems
Food & Beverage
Sanitary designs with PTFE coatings for contamination-free processing
Pharmaceutical
High-precision control in clean environments
Pulp & Paper
Withstands abrasive slurries and chemicals
Pipeline Preparation
Ensure flanges are aligned to prevent stress and leakage.
Pre-Installation Inspection
Check components for cleanliness and integrity before installation.
Valve Positioning
Install in the closed position for proper seating.
Actuator Alignment
Ensure correct orientation and alignment with valve body before tightening.
Bolt Tightening
Apply even torque across all bolts for a secure seal.
Air Pressure
Supply air at standard pressures (typically 0.4–0.6 MPa).
Manual Testing
Manually operate the solenoid for initial movement checks.
Stroke Adjustment
Fine-tune actuator stroke if the valve sticks at the beginning of travel.
Smooth Operation
Ensure unobstructed disc movement and proper sealing.
Speed Control
Use adjustable flow restrictors to control actuator speed. Avoid over-restricting.
Routine Inspections
Check seals, actuators, and solenoid valves regularly.
Lubrication
Periodically lubricate moving parts in harsh environments.
Seal Replacement
Replace worn seals to maintain leak-free performance.
Actuator Care
Inspect for air leaks or sluggish behavior; clean air lines and solenoids as needed.
Service Records
Maintain documentation for tracking performance and anticipating issues.
Pneumatic wafer butterfly valves are indispensable for efficient and precise fluid control in diverse industries. Their innovative design, reliable performance, and adaptability to various media and environments make them a go-to solution in modern systems.
From rapid actuation to durable sealing, these valves are engineered for performance and long-term reliability. When installed and maintained properly, they contribute to operational safety, efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs.
Choosing a high-quality valve and following best practices in installation and upkeep ensures maximum system performance and a solid return on investment.Know more about Google SEO Directory
